Sustainable Glossary: Key Sustainability Terms
At the heart of sustainable marketing are concepts and practices that help businesses balance profit with purpose. A specialised vocabulary has emerged to describe complex ecological concepts and initiatives. In this blog, we have put together a useful glossary of key terms and ideas.
Glossary of Key Sustainability Terms
Triple Bottom Line
Sustainable marketing takes a holistic approach by promoting products and services that are not only profitable but also socially and environmentally responsible. This aligns with the triple bottom line concept in business, which emphasises balancing economic, social and environmental factors when making business decisions and measuring success.
Circular Economy
A circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development that goes beyond traditional linear business models by considering the entire lifecycle of a product. By focusing on eliminating waste and promoting continual resource use, businesses can minimise their environmental impact and maximise resource efficiency to benefit businesses, society and the environment.
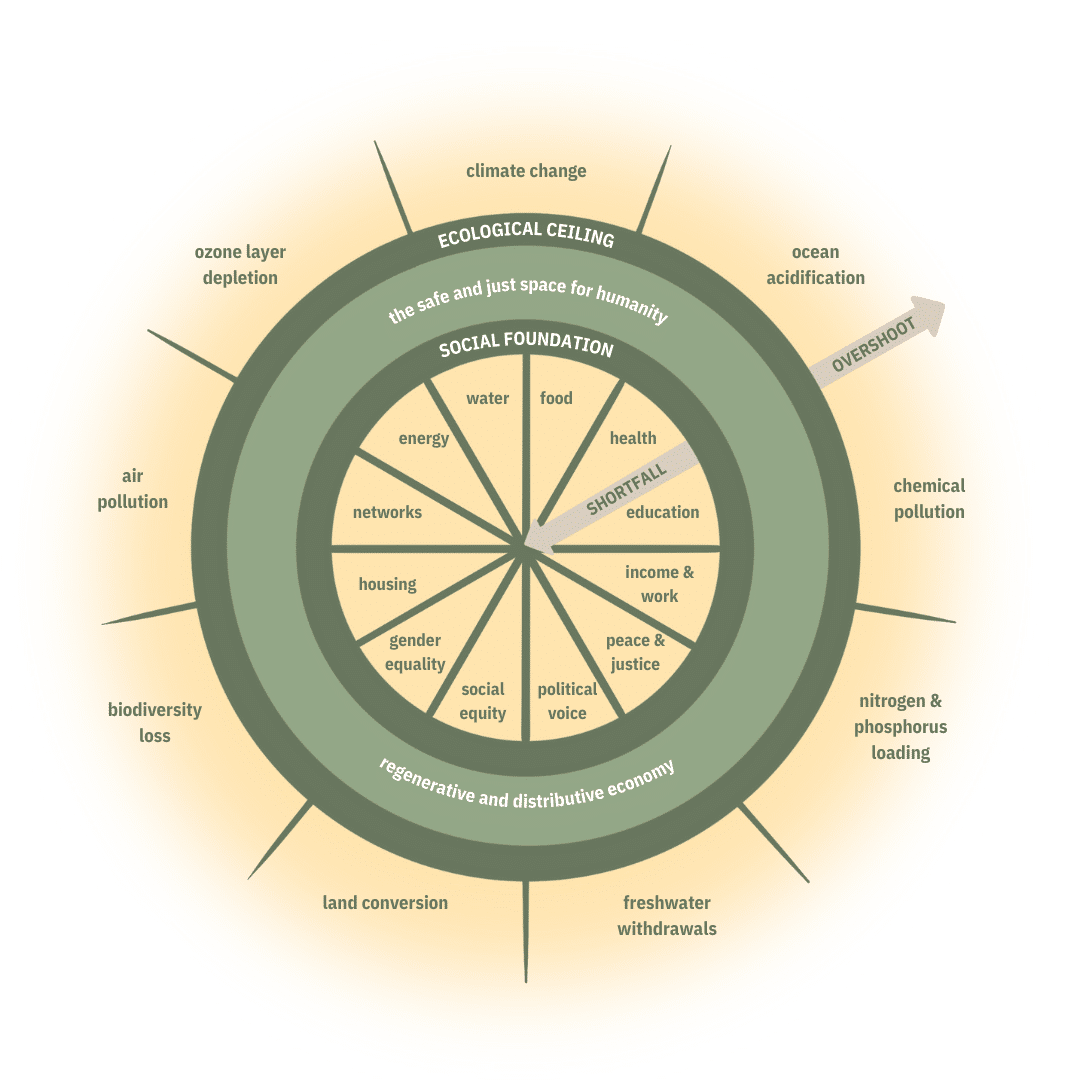
Planetary Boundaries
Planetary boundaries are a framework within which humanity can continue to develop without compromising the future of our planet. Crossing these boundaries will result in irreversible environmental changes with detrimental consequences for humankind. The concept of planetary boundaries outlines nine environmental limits within which humans can safely operate:
- Climate change
- Change in biosphere integrity (biodiversity loss and species extinction)
- Stratospheric ozone depletion
- Ocean acidification
- Biogeochemical flows (phosphorus and nitrogen cycles)
- Land-system change (e.g. deforestation)
- Freshwater use
- Atmospheric aerosol loading (microscopic particles in the atmosphere that impact the climate and living organisms)
- Introduction of novel entities
Doughnut Economics
Doughnut economics provides a visual framework for balancing social needs with ecological limits, ensuring everyone has access to life’s essentials without overstepping the nine planetary boundaries.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The SDGs, established by the UN, encompass 17 interconnected goals serving as “a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future”. By aligning business objectives with these goals, sustainable marketing drives action that contributes to global sustainability. As outlined by the UN, the 17 SDGs are:
- Eradicate poverty in all its forms everywhere
- End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Promote well-being for all at all ages and ensure healthy lives
- Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
- Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
- Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and foster innovation
- Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
- Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
- Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development
- Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat deforestation, halt and reverse land degradation, and halt biodiversity loss
- Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
- Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalise the global partnership for sustainable development
Tragedy of the Commons
The tragedy of the commons illustrates how individual self-interest can lead to the depletion of communal resources, highlighting the need for collective action and responsible consumption. Sustainable marketing plays a critical role in promoting collective responsibility and stewardship of shared resources to avoid overconsumption, underinvestment, and depletion of these resources.
Cradle-to-Cradle
This sustainable design philosophy encourages the creation of products with their entire lifecycle in mind. In line with the circular economy approach, cradle-to-cradle means designing products for continuous cycles of use, with materials and components that can be repurposed or recycled indefinitely.
Natural Capital
An important aspect of sustainable marketing is recognising the economic value of nature and incorporating its conservation into business strategies. Natural capital describes the world’s stocks of natural assets, including geology, soils, air, water and all living organisms.
Resiliance Theory
Resilience theory focuses on the capacity of systems – whether ecological, social, or economic – to absorb disturbances and adapt to change. In terms of sustainable marketing, this means building adaptable business models that can buffer change and thrive amidst environmental and social shifts.
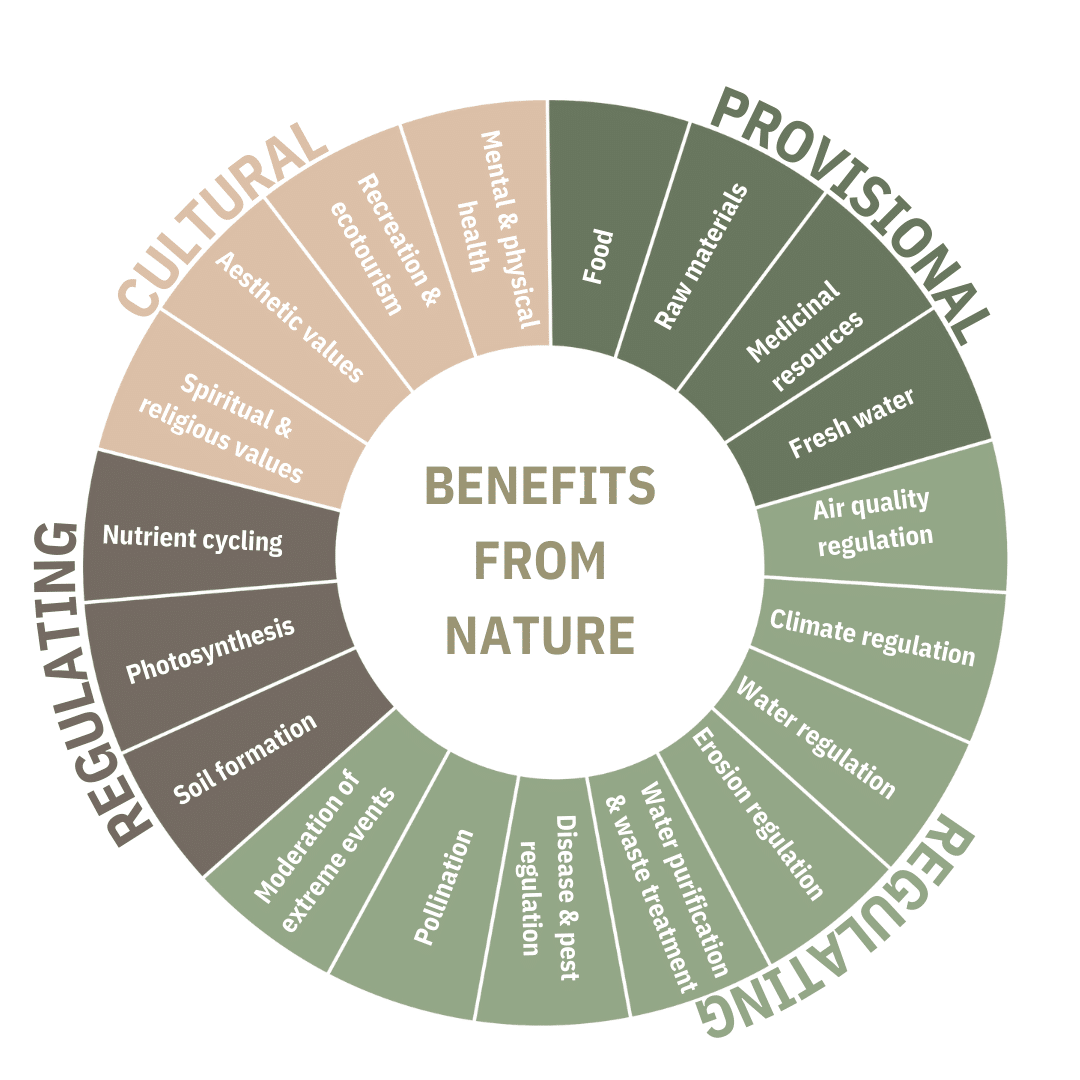
Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the direct and indirect benefits humans gain from the natural environment and properly functioning ecosystems. From providing food and water to reducing stress and anxiety, it’s difficult to quantify the value of these services to humankind. Sustainable marketing aims to promote environmental stewardship to protect and enhance these services.

Degrowth
Degrowth is a social movement that calls for reduced production and consumption, prioritising social and ecological well-being instead of profits. Sustainable marketing is a vital catalyst for steering mass consumption towards conscious consumerism, by educating buyers and promoting products that are sustainable and durable.
Biomimicry
This design philosophy draws inspiration from nature, learning from and mimicking the strategies found in the natural world for sustainable solutions. Biomimicry emphasises recognising what we can learn from nature, rather than what we can extract.
Green Economy
A green economy is low-carbon, resource-efficient and socially inclusive, aiming for sustainable development without degrading the environment. Sustainable marketing accelerates the transition to a green economy by promoting products and services that contribute to environmental health and social well-being.
Environmental Justice
Environmental justice ensures that all people, regardless of race, colour, nationality or income, have the same degree of protection from environmental and health hazards as well as equal involvement in decision-making regarding the implementation and enforcement of environmental policies.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
CSR refers to businesses taking responsibility for their impact on society and the environment. Transparency is a key aspect of sustainable marketing, ensuring companies demonstrate their authentic commitment to sustainability.
Sustainable marketing isn’t just a buzzword, it involves revolutionising business strategies to align with broader goals of sustainability and social responsibility. Rooted in these key concepts, sustainable marketing is the pathway to achieving a balance between economic success, social well-being, and environmental health.
- https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-the-triple-bottom-line
- https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/the-circular-economy-in-detail-deep-dive#:~:text=A%20circular%20economy%20is%20a,the%20consumption%20of%20finite%20resources.
- https://www.un.org/en/exhibits/page/sdgs-17-goals-transform-world#:~:text=GOAL%201%3A%20No%20Poverty%20GOAL,10%3A%20Reduced%20Inequalities%20GOAL%2011
- https://earth.org/what-is-tragedy-of-the-commons/
- https://c2ccertified.org/
- https://naturalcapitalforum.com/about/#:~:text=Natural%20capital%20can%20be%20defined,which%20make%20human%20life%20possible.
- https://degrowth.info/degrowth
- https://biomimicry.org/what-is-biomimicry/
- https://www.unep.org/regions/asia-and-pacific/regional-initiatives/supporting-resource-efficiency/green-economy
For more information on how sustainability can benefit your business, get in touch with a member of the team at growfish.co.
Related Posts
Sustainability in Ibiza: Building a Resilient Local Economy
Like many popular holiday destinations in Spain, the “party island” Ibiza, is suffering from the environmental and social consequences of mass tourism. However, a growing number of local initiates and businesses are laying the foundation for a more environmentally...
Sustainable Marketing in Spain: Revolutionising the Tourism Industry Amidst Anti-Tourism Protests
Spain, with its rich history and stunning landscapes has established itself as one of the world's top tourist destinations. However, the country now finds itself battling with the consequences of its own success. The recent protests across Barcelona, Majorca and the...
Sustainable Marketing in Bali: Transforming the Tourism Industry
With its stunning landscapes and rich cultural traditions, Bali has long been a top tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year. However, the exponential growth of mass tourism in Bali raises concerns about environmental degradation, cultural...




